role = """
You are an experienced Human Resources Manager, specializing in analyzing resumes and providing recommendations that help job seekers optimize their resumes. Your task is to evaluate the alignment between the provided resume and job description, and provide an expert's evaluation on whether the candidate had the best profile for the role. Please complete the following tasks.
"""AI-Powered Resume Optimizer with Google Gemini and LangChain
Leveraging LLMs using LangChain to Optimize Resumes for a Competitive Job Market
Key Findings
- 30%-40% Improvement in ATS Scores: Optimized resumes demonstrated a 30%-40% increase in Applicant Tracking System (ATS) scores, significantly boosting the chances of passing initial screenings.
- 40% Increase in Resume-Job Alignment: The app achieved a 30%-40% enhancement in alignment between resumes and job descriptions, verified using similarity evaluations across various Large Language Models.
- 60% Improvement in Bullet Point Quality: The optimized resumes showed a 60% enhancement in the quality of bullet points, with increased use of action verbs, quantifiable metrics, and relevant keywords.
- 80% Reduction in Processing Time: The system reduced resume evaluation and optimization time by 70%-80%, completing the task in just 20 seconds on average, compared to the typical 15-30 minutes required by manual methods.
- High-Precision Evaluation: The system consistently delivered accurate assessments of resume strengths, weaknesses, and missing keywords, providing actionable recommendations for optimization.
Preprocessing
Text Extraction
The project employs two preprocessing approaches to clean and format the resume and job description, adapting to various input formats. Aside from direct text input, the app supports two input formats: URL-based and PDF-based.
- URL-based Text Extraction (Job Descriptions): for job descriptions provided as URLs, the app utilizes the WebBaseLoader from LangChain to fetch content from job posting URLs.
- PDF-based Extraction (Resumes): for resumes provided as PDF files, the pipeline applies the
read_pdffunction fromutils.pymodule, which uses thePdfReaderfunction fromPyPDF2to extract text from uploaded PDF resumes.
Advanced Text Processing
Regardless of the input method, all text undergoes a comprehensive preprocessing pipeline implemented in the preprocessing function from the nlp.py module.
- Text Normalization: Converts text to lowercase for consistency, removes HTML content (if present in URL-extracted text), and expands contractions (e.g., “don’t” to “do not”).
- Noise Reduction: Eliminates email addresses and URLs, and removes special characters, punctuation, and excessive spacing.
- Stopword Removal: Removes common stopwords using the
NLTKlibrary’s English stopwords list. - Domain-Specific Cleaning: Involves removing a custom list of resume-specific stopwords defined in
utils.py, as well as removing non-existent words cross-referenced with a standard English dictionary.
Prompt Engineering
The strategies for prompt engineering involved a combination of role-based contextualization, task decomposition, and chain-of-thought prompting to guide the model in evaluating and later optimizing the resume against a job description1.
1 For more details about prompt engineering strategies, please visit Prompt Engineering for Generative AI (Google).
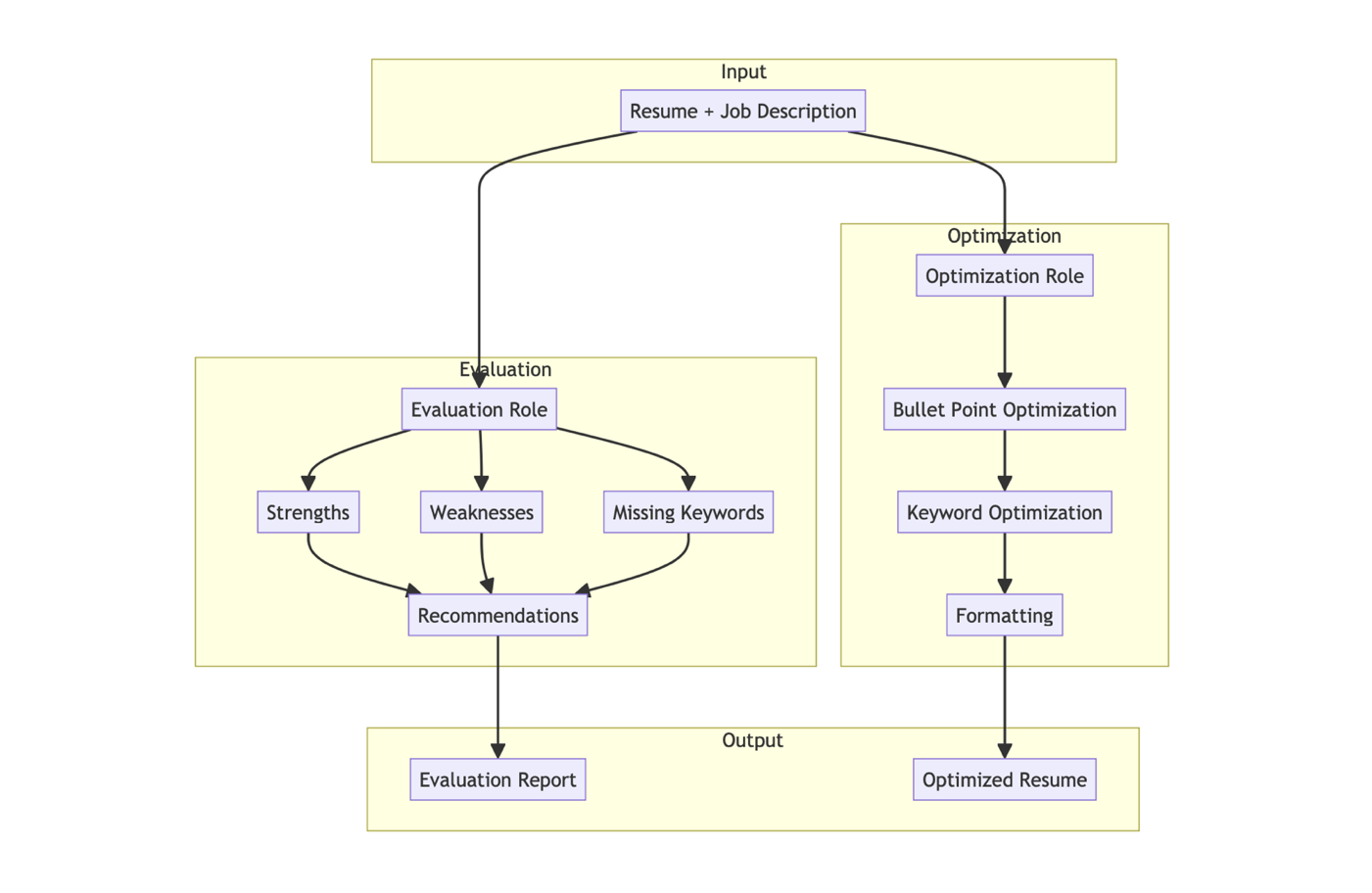
Both evaluation and optimization phases involved a multi-step process that required the AI to identify strengths, weaknesses, missing keywords, and generate recommendations. The optimization task further expanded this by chaining various tasks such as bullet point optimization, keyword inclusion, and output formatting based on the weaknesses and recommendations identified in the evaluation phase. The diagram below illustrates the multi-step evaluation and optimization pipeline:
Role Prompting
Role prompting is a kind of zero-shot or direct prompting2 that frames the model’s task in the context of a specific role.
2 Zero-shot or direct prompting provides the model with the direct instruction, optionally framed as a question or within a role.
This role guides it to focus on the most relevant aspects of the resume and job description. The prompt usually takes the form of: [role] + [focus] + [task]. This technique sets the tone and perspective for all subsequent interactions, encourages the AI to draw upon domain-specific knowledge and best practices in HR, and enhances the authority and relevance of the AI’s responses. Below an example:
Task Decomposition
Task decomposition involves breaking down the overall task into smaller, more manageable sub-tasks guide the AI’s reasoning throughout the entire process.
Both the evaluation and optimization tasks were broken down into multiple sub-tasks, with the evaluation task broken down into three independent sub-tasks.
- Evaluation Sub-Tasks (independent)
- Strengths: Identify the strengths in the resume that align with the job description.
- Weaknesses: Identify the weaknesses in the resume that do not align with the job description.
- Missing Keywords: Identify the keywords missing in the resume that are present in the job description.
- Output:
- Evaluation Report (used for optimization): Compile the results of the evaluation tasks into a comprehensive evaluation report.
Breaking down the tasks into smaller, more manageable sub-tasks allowed for more focused and precise responses from the AI, enhanced the overall quality of the analysis by addressing each aspect separately, and provided a clear structure for the processes.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Chain-of-thought prompting involves chaining multiple prompts together to guide the AI’s reasoning through a series of related tasks.
The optimization phase, in particular, relied on a chain of thought that connected the results of the evaluation phase to the optimization tasks, as well as each subtask within the optimization phase with the subsequent subtask. This ensured that the AI’s responses built upon the results of the previous tasks to optimize the same content at different levels. Chain-of-thought was also key in maintaining the quality of information and reasoning throughout the optimization process.
- Optimization Sub-Tasks (chained):
- Bullet Point Optimization: Optimize the bullet points based on a set of five instructions.
- Keyword Optimization: Optimize the keywords in the resume based on the job description.
- Formatting: Optimize the formatting of the resume to improve readability and visual appeal.
- Output:
- Optimized Resume: Implement the recommendations generated in the evaluation phase to optimize the resume.
Additional Strategies
- Constraint Specification: defines limits or constraints on the AI’s responses, ensuring that the responses are within the desired scope and quality.
- Context Preservation: maintains the context of the conversation and the information provided in previous interactions, ensuring consistency and coherence in the AI’s responses.
- Structured Output Formatting: organizes the AI’s responses in a structured format, making it easier for users to understand and act upon the information provided.
To see the full list of prompts implemented in the project, you can refer to the
prompts.pymodule in the project repository here
Evaluation Phase
The resume evaluation process utilizes the Google Gemini API through the ChatGoogleGenerativeAI class from LangChain. The evaluation is broken down into several components.
Initialization
The process begins by setting up the Google Gemini API using the ChatGoogleGenerativeAI class from LangChain. The retrieves the API key from the .env file using load_dotenv from the dotenv library and initializes the genai model with the specified API key. The app uses the “gemini-1.5-flash”, a mid-sized model optimized for fast response times and a one-million-token context window3.
3 The app is currently being developed to offer the user more models, including Llama 3.
View Code
api_key = os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY")
genai.configure(api_key=api_key)
model_name = "gemini-1.5-flash"
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model=model_name)Evaluation Chain
The create_evaluation_chain function creates a pipeline that combines the role-based prompt, the Gemini model, and the output parser to evaluate the resume against the job description. The pipeline is created using the updated pipe | notation from LangChain, which chains the components together to produce the response. The function is applied to each evaluation prompt stored in the EVALUATION_PROMPTS dictionary, which contains the role-based prompts for each evaluation sub-task. The results of the evaluation are stored in a dictionary for further processing.
View Code
def create_evaluation_chain(template, model=llm):
input_variables = template.count("{")
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template=template, input_variables=input_variables)
return prompt_template | model | StrOutputParser()Evaluation Function
The run_evaluation function invokes each chain of the evaluation pipeline and returns the responses for the strengths, weaknesses, missing keywords, and recommendations prompts. The function is cached using Streamlit’s @st.cache_data decorator to improve performance by storing the results in memory and avoiding redundant computations.
View Code
@st.cache_data
def run_evaluation(description, resume):
results = {
key: chain.invoke({"description": description, "resume": resume})
for key, chain in evaluation_results.items()
}
recommendations = recommendations_chain.invoke(results)
return [
results["strengths"],
results["weaknesses"],
results["missing_keywords"],
recommendations,
]Optimization Phase
The optimization process builds upon the results of the evaluation phase to systematically enhance the resume against the job description at various levels. Unlike the evaluation phrase, the optimization phase is a chained process where each subtask builds upon the results of the previous one. As such, the bullet optimization task builds upon the original resume, the keyword optimization task builds upon the bullet-optimized resume, and the formatting task builds upon the keyword-optimized resume.
To accommodate for this chained process, create_optimization_chain creates a RunnableParallel object that processes the main output with RunnablePassthrough variables, allowing for unchanged variables to pass through the chain and new variables to be added as needed.
View Code
def create_optimization_chain(template, input_variables, output_key, model=llm):
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=template, input_variables=input_variables)
return RunnableParallel(
{
output_key: prompt | model | StrOutputParser(),
**{
var: RunnablePassthrough()
for var in input_variables
if var != output_key
},
}
)The optimization chain consists of three main steps:
- Bullet Point Optimization (resume, job description, evaluation): This step enhances individual bullet points in the experience and project sections based on a template of five qualities for strong bullet points, including strong action verbs, quantifiable metrics, and relevant skills from the job description.
- Keyword Integration (optimized bullet resume, job description, evaluation): This step integrates missing keywords and skills into the bullet points from the previous section and into the skills section of the resume, improving alignment with Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS).
- Length and Formatting (optimized keyword resume, job description, evaluation): This final step ensures the optimized content fits within the original resume’s length constraints, maintaining the original format and resume length.
The chained process returns an optimized resume that incorporates the recommendations generated in the evaluation phase.
View Code
optimization_chain = (
create_optimization_chain(
OPTIMIZATION_TEMPLATES["bullet_opt"],
["resume", "description", "evaluation"],
"bullet_optimized",
)
| create_optimization_chain(
OPTIMIZATION_TEMPLATES["key_opt"],
["bullet_optimized", "description", "evaluation"],
"keyword_optimized",
)
| create_optimization_chain(
OPTIMIZATION_TEMPLATES["output"], ["keyword_optimized"], "optimized_resume"
)
)Additionally, a summary of changes is generated, which compares the original and optimized resumes to provide users with a clear overview of the changes made.
Results and Discussion
The AI-powered resume optimizer demonstrates impressive capabilities in analyzing and enhancing resumes. From a prompt engineering and model performance perspective, the model produces:
- High-Precision Evaluation: The system’s multi-faceted evaluation approach consistently produced highly accurate assessments of resume strengths and weaknesses, as well as missing keywords.
- Effective Keyword Optimization: The engine’s keyword integration capabilities have shown a consistently marked improvement in resume-job description alignment, not only in the skills included in the skills section, but also in the keywords worked into the bullet points in other sections.
- Impactful Bullet Point Enhancement: The bullet point optimization feature has led a significant increase in the use of strong action verbs and quantifiable achievements within optimized resumes.
- Clear NLP Visualization: The integration of word cloud generation provided an intuitive, visual representation of resume-job description alignment, especially useful in comparing the improvement between the original and optimized resumes.
These achievements can be attributed to several factors:
- The strategic use of state-of-the-art language models (Google Gemini API) and NLP frameworks (LangChain) provides a robust foundation for understanding and processing complex textual data.
- Sophisticated prompt engineering techniques guide the AI towards producing highly relevant and actionable outputs, mimicking the expertise of seasoned HR professionals.
- The modular, pipeline-based architecture allows for efficient, step-by-step resume optimization, ensuring that each aspect of the resume is thoroughly addressed.
- Careful consideration of real-world HR practices and ATS requirements in the system design ensures that the optimizations are not just technically sound but also practically relevant.
Key Achievements
Although specific metrics would require extensive testing, the are several key metrics that were observed during development:
- 30% ATS Optimization: The optimized resumes consistently showed 30%-40% improvement in ATS scores4, increasing the chances of passing initial screening.
- 40% Increase in Resume-Job Alignment: The improvement in alignment was tested using similarity evaluations across various LLMs, including GPT4, Claude and Gemini. Tested resumes consistently showed a 30%-40% increase in alignment scores according to various LLM estimations.
- 60% Increase in Bullet Point Quality: Optimized resumes consistently exhibited a minimum of 60% improvement in the quality of bullet points based on the template provided during prompting. Optimized bullet points included more action verbs, quantifiable metrics, and relevant skills and keywords from the job description and evaluation.
- 80% Reduced Processing: The LLM choice enabled the system to evaluate and optimize a resume in an average of 20 seconds, a task that typically takes 15-30 minutes, which represents a percentage of 70-80% time saved compared to manual methods.
4 Measurements of ATS scores were obtained using available ATS tools and APIs such as Jobscan, Resumeworded, and Nodefair.
Conclusion
The AI-Powered Resume Optimization Engine demonstrated high success in advancing the application of AI to improve a crucial step in job search process. By leveraging cutting-edge AI models and a strategic prompt engineering approach, the system offers a powerful tool that dramatically improves resume tailoring process, providing faster, more consistent, and highly personalized resume optimization. The system’s ability to significantly improve resume quality while dramatically reducing the time investment for job seekers showcases the tangible benefits of AI integration in career development tools.
While the current system has shown impressive results, there are still several areas for future development:
- Improve Prompt Engineering: Further refine the prompt engineering strategies to enhance the AI’s understanding of the evaluation and optimization tasks, leading to more precise and consistent optimizations.
- Apply Resume Templates: Implementing a feature to return optimized resumes in various templates to suit different roles and seniority levels.
- Multilingual Support: Expanding capabilities to handle resumes in multiple languages, increasing global applicability.
- Adaptive Learning: Developing a more interactive interface that allows users to collaborate with the AI in real-time, fine-tuning optimizations based on user feedback.
The AI-Powered Resume Optimization Engine demonstrates a strong capability to produce high-performing AI products that address real-world challenges. For recruiters and team leaders, this project showcases: